Description
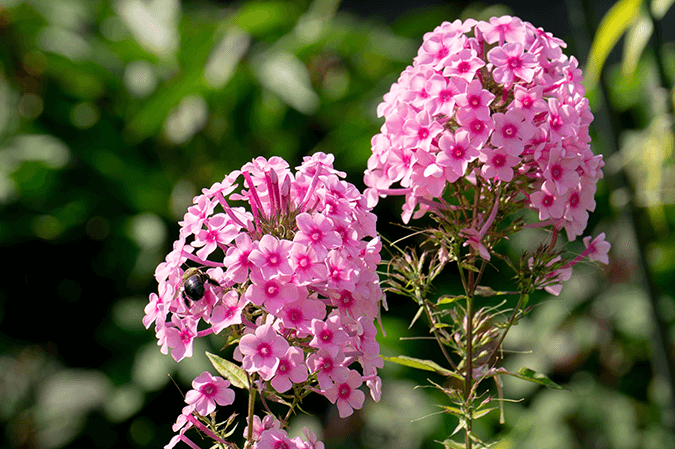
Phlox is a genus of flowering plants in the family Polemoniaceae. The genus includes about 67 species, most of which are native to North America. Phlox plants are known for their vibrant, colorful flowers that bloom in clusters. These flowers can be found in a wide range of colors, including pink, purple, red, white, and blue. Depending on the species, phlox can be annual or perennial, and their growth habit can range from low-growing ground covers to tall, upright plants.
Common Features
- Leaves: Phlox leaves are typically opposite, meaning they grow in pairs on either side of the stem. They are usually lance-shaped and can be either smooth or slightly hairy, depending on the species. The leaves are often a medium to dark green, providing a lush backdrop to the bright flowers.
- Flowers: The flowers of phlox are five-petaled and star-shaped, often forming dense, fragrant clusters. They vary in size, with some species producing tiny flowers while others have blooms up to an inch in diameter. The color of phlox flowers is one of their most appealing features, ranging from pure white to deep red and even shades of lavender and blue.
- Growth Habit: Phlox species exhibit a variety of growth habits. For instance, Phlox subulata (creeping phlox) forms a dense, mat-like ground cover, while Phlox paniculata (garden phlox) grows upright and can reach heights of 2 to 4 feet. This diversity in growth habits makes phlox a versatile plant for various garden settings.
- Fragrance: Many phlox species are known for their pleasant fragrance, particularly in the evening. This makes them popular in gardens designed to attract pollinators and provide sensory appeal.
Role in the Ecosystem
- Pollination: Phlox flowers are highly attractive to pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds. Their bright colors and sweet fragrances draw these creatures, facilitating cross-pollination. This not only helps the phlox reproduce but also supports the local pollinator population.
- Wildlife Habitat: Phlox provides habitat and food for various insects and small animals. For example, the leaves of phlox plants are a food source for the larvae of some butterfly species. Additionally, ground-covering phlox species can offer shelter to small creatures.
- Soil Stabilization: Ground-covering species like Phlox subulata are effective in stabilizing soil, particularly on slopes and embankments. Their dense root systems help prevent soil erosion by holding the soil in place.
Importance
- Ornamental Value: Phlox is a popular ornamental plant in gardens and landscapes due to its colorful and abundant blooms. It is often used in borders, rock gardens, and as ground cover. The long blooming season of many phlox species makes them a valuable addition to gardens, providing continuous color throughout the growing season.
- Cultural Significance: In the language of flowers, phlox represents harmony and sweet dreams. It is often included in bouquets and floral arrangements for its beauty and symbolism. Garden phlox, in particular, has been a favorite in cottage gardens and traditional landscapes for centuries.
- Medicinal Uses: While not widely used in modern medicine, phlox has been used traditionally by Native Americans for various purposes. Some species were used in herbal remedies to treat skin conditions and digestive issues. However, these uses are not well-documented in contemporary herbal medicine.
- Biodiversity Support: By attracting a wide variety of pollinators and providing food and habitat for insects, phlox plays a significant role in supporting local biodiversity. This makes it an important plant for ecological gardening and habitat restoration projects.
Interesting Facts
- Phlox in the Wild: In the wild, phlox is often found in prairies, woodlands, and alpine regions. Phlox drummondii, known as Drummond’s phlox, is a wildflower native to Texas and is the only annual species commonly grown in gardens.
- Name Origin: The name “phlox” comes from the Greek word for flame, likely referring to the bright, fiery colors of the flowers.
- Creeping Phlox’s Popularity: Phlox subulata is particularly popular in rock gardens and as a ground cover due to its low-growing habit and the vibrant carpet of flowers it produces in the spring.
Sources
- Missouri Botanical Garden. (n.d.). Phlox – Plant Finder. Retrieved from MBG
- Royal Horticultural Society. (n.d.). Phlox – Plant Care and Growing Guide. Retrieved from RHS